What is Superior Tibiofibular Joint Sprain
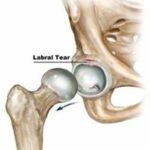
The Superior tibiofibular joint is also known as the Proximal Tibiofibular Joint. The joint is formed between the tibia and fibula (lower leg bones) immediately below and outer side of the knee.
This joint allows twisting movements of the leg, as well as, load transfer between the feet and the rest of the body. The joint is surrounded by Ligaments and joint capsules. These structures offer stability to the joint during movement and weight-bearing activities.
The Peroneal Nerve (a nerve that supplies the lower leg and toes) runs around the neck of the fibula and can also be injured, in superior tibiofibular joint injury cases.
Causes of Tibiofibular Joint Sprain
The superior tibiofibular joint is most commonly injured following a traumatic incident involving the knee.
Other causes of Superior Tibiofibular Joint Sprain in this area include :
- Osteoarthritis;
- Poor biomechanics of the knee and ankle joints.
- Muscle imbalances in the lower limb.
- Repetitive forces going through the knee and ankle like in jumping.
- Presence of a physical lesion, e.g. Ganglion, Neoplasms.
- Hypo-mobility (not enough movement) of the tibiofibular joint
- Hyper-mobility (too much movement) of the tibiofibular joint
- Fatigue
Symptoms of Superior Tibiofibular Joint
The superior tibiofibular joint injury may or may not occur with other injuries to the knee.
Common symptoms of a Superior Tibiofibular Joint Sprains include:
- Pain on the outer aspect of the knee
- Redness and swelling on the outside of the knee
- Pain is aggravated by weight-bearing activities, especially high loading activities.
- Feelings of weakness or giving way around the knee
Contact PAIN-FREE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC to know more about any knee problem and best possible treatment for the condition.
Diagnosis:
The Physiotherapist will look for signs and symptoms related to superior tibiofibular joint injury. Tenderness over the joint region and stress tests are sufficient to diagnose the condition.
An MRI may be required to confirm the diagnosis and rule out injury to other nearby structures.
Treatment:
- Physiotherapy
Most patients with a Superior Tibiofibular Injury start to recover within a few weeks of the injury with the appropriate rehabilitation.
The Physiotherapy treatment will aim to:
- Reduce pain and inflammation
- Normalize joint range of motion
- Strengthen the muscles of the lower limb
- Improve patellofemoral (knee cap) alignment
- Normalize muscle lengths/ stretching exercises
- Improve proprioception and balance
- Improve functionality e.g. walking, running, squatting, jumping
- Minimize chances of re-injury
Physiotherapy Clinic in Dwarka advises that one should discuss the knee injury with a knee injury specialist such as a physiotherapist or knee surgeon.
- Surgery
Normally superior tibiofibular sprains resolve completely with conservative treatment. Depending on the severity and involvement of other structures, surgery may be required.
As will all cases of knee surgery risk may include pain, infection, instability, stiffness, and difficulty returning to the previous level of activity.
Post-Surgical Rehabilitation:
For a quick and successful recovery, Post-operative Knee Rehabilitation is one of the most important aspects which is often neglected after knee surgery.
The rehabilitation following knee surgery focuses on restoring full knee range of motion, strength, power, endurance, balance and proprioception, and agility training that is individualized to specific sporting or functional needs.
Prevention:
The things that should be done to reduce the risk of sustaining a superior tibiofemoral injury includes-
- Biomechanical correction of the knee and ankle joint.
- Adequate warm-up and stretching program before and after exercise.
- muscle imbalance correction in the lower limb
- Adequate footwear during exercise
- Avoid sudden increases in training frequency and/or intensity
- Strengthening lower limb muscles.
Can we Return to Sports with a Superior Tibiofibular Joint Sprain?
Yes, With a suitable rehabilitation regime, the patient can be successfully rehabilitated back to normal life or sporting activity.