How to Treat a Labral Tear (Hip) for Faster Healing
Labral Tear (Hip): Effective Treatment Methods
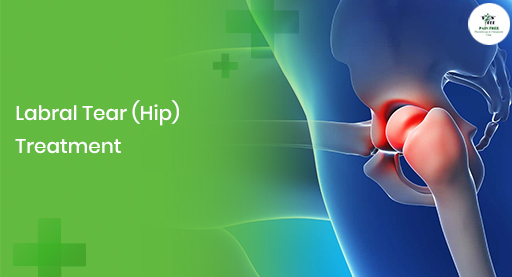
The margins of the socket part of the hip joint are attached with a cartilaginous rim around it to deepen the socket known as the labrum. The purpose of the cartilaginous rim is to provide greater stability to the joint. The labrum can get torn and produce pain and clicking sound and hence need for a Labral Tear Hip Treatment.
Causes
A labral tear can result from repetitive strain injury in activities that require frequent rotations at the hip like golf, ballet dancing or contact sports.
Sudden fall or traumatic injury to the hip
Sports in which hip joint is taken to extreme ranges can cause labral tear.
Note: Researches suggests approximately 22% of athletes who complain of groin pain have a labral tear in the hip. However, almost 75% of cases acetabular labrum tears have no direct known cause.
Symptoms
Some patients may experience “a catch” with hip movements.
Diagnosis
An assumption can be made on the basis of the patient’s signs and symptoms and on the basis of physical examination. But to confirm the diagnosis an MRI is needed most of the time.
Labral Tear Hip Treatment :
Physiotherapy management
STAGE I – PAIN RELIEF AND PROTECTION
Avoid activities that aggravate the symptoms. Rest the hip joint in a comfortable position. Various physiotherapy means can be implemented to reduce the pain.
Patient with labral tear should avoid sitting:
- With knees lower than the hip joint.
- Crossed legs or hips in a rotated position.
- on the edge of the seat/ chair
- Brisk walking (excess hip extension)
STAGE II – RESTORE FLEXIBILITY AND STRENGTH
The physiotherapist work on the following areas to further improve the condition of the patient,
- Restoration of limited joint range-of-motion.
- Restoration of the soft tissue muscle length and resting tension.
- Activation of deep stability muscles of the hip.
- Enhancement of the proprioception and joint position sense.
STAGE III – RETURN TO NORMAL ACTIVITY/ SPORTS
- Focus in on enhancement of functional activities of daily living (ADLs)
- A Graduated sports program that is specific to the needs of the patient.
- Agility, speed, power, and sport-specific drills.
Most of the labral tear cases can be managed by conservative treatment while some may need hip surgery.
Surgical Labral Tear Hip Treatment :
The detached segment of the labrum can either be re-attached or be debrided depending upon the extent of the labral tear.
Post-operative hip rehabilitation under the guidance of an expert physiotherapist is needed to facilitate a safe return to sport.