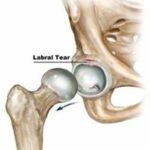
What is Runner’s Knee?
As the name suggests Runner’s Knee is Knee pain commonly suffered by runners but it may also affect people with constant knee bending activity. Runner’s knee can be a result of one of the numerous knee injuries.
Runner’s knee can be categorized into either Anterior knee pain (front) or Lateral knee pain (outer aspect) commonly affecting the runners.
Causes of Runner’s Knee
Anterior Runner’s Knee Pain Sources,
Anterior knee pain is felt on the front of the knee, and the most common conditions in runners are often managed effectively with pain free physiotherapy.
- Patellofemoral Joint Pain Syndrome
- Chondromalacia Patella
- Patella Tendonitis
- Knee Bursitis
- Fat Pad Syndrome
Lateral Runner’s Knee Pain
Lateral knee pain is felt on the outer aspect of the knee and the most common cause in runners is Iliotibial band (ITB) syndrome.
Symptoms of Runner’s Knee:
Runner’s knee strikes mostly younger, recreational runners and twice as many women as men, according to the British Journal of Sports Medicine. (Women tend to have wider hips, resulting in a greater angling of the thighbone to the knee, which puts the kneecap under more stress).
Symptoms of runner’s knee include–
Tenderness behind or around the patella, usually toward its center,
Pain toward the side of the knee, a sense of cracking or that the knee’s giving way,
Steps, hills, and uneven terrain can aggravate the runner’s knee.
Diagnosis:
Physiotherapists are experts in the diagnosis of a runner’s knee. For an accurate diagnosis, please seek a professional opinion since treatment can vary considerably depending on the diagnosis.
Treatment of Runner’s Knee:
Runner’s knee treatment will vary according to the specific underlying condition. As discussed earlier it may arise as a result of the following conditions mentioned below, treatment will be accordingly.
- Patellofemoral Joint Pain Syndrome
- Chondromalacia Patella
- Patella Tendonitis
- Knee Bursitis
- Fat Pad Impingement
- Iliotibial band (ITB) syndrome
Each of these conditions requires a personalised approach that may include rest, strengthening exercises, pain free physiotherapy, and activity modifications to ensure effective recovery and long-term knee health.
In most cases, a physiotherapy plan focuses on improving knee alignment, reducing inflammation, and strengthening the surrounding muscles to support joint stability. Taping techniques, manual therapy, and guided stretching may also be included as part of the rehab process. With consistent care and the right guidance, patients often return to their normal routine without pain or limitations.