What is Soft Tissue Massage

It was not until the 16th century that some of the soft tissue techniques used in the earliest days were used again for medical practice. Though it took another 200 years i.e. until the 18th century, massage becomes popular throughout Europe. The era of modern massage is said to have begun during the early 1800s and by the 1900s massage was used in most parts of the developed world.
It can be broadly classified into–
- Recreational massage and
- Therapeutic massage
William Murrell (1853-1912) defined massage as a “scientific method of treating certain forms of a disease by systematic manipulation”.
Beard (1952) – “the term use to designate certain manipulation at the soft tissue of the body; these manipulations are most effectively performed with the hands and are administered for the purpose of producing effects on the nervous, muscular and respiratory system and the local and general circulation of blood and lymph”.
EFFECTS OF MASSAGE
- Mechanical
- Physiological
- Psychological
- Therapeutic
Mechanical effects:
- Movement of blood, lymph, venous blood, lung secretions, edema, intestinal content, and hematoma contents.
- Mobilization of muscle fibers, muscle mass, tendons, tendon sheath, skin and subcutaneous tissue, scar tissue, and adhesions.
Physiological effects:
- Increase blood and lymphatic flow
- Increase flow of nutrition
- Removal of waste products and metabolites
- Stimulation of healing process
- Resolution of chronic oedema and hematoma
- Increased extensibility of connective tissue
- Pain relief
- Increased joint movement
- Facilitation of muscle activity
- Stimulation of autonomic nervous system
- Stimulation of visceral function
- Removal of lung secretions
- Sexual arousal and
- General relaxation
Psychological effects
- Physical relaxation
- Relief from anxiety and tension
- Stimulation of physical activity
- Pain relief
- A general feeling of well being
- General faith in physiotherapist
Therapeutic effect
- Enhance absorption of waste products
- For chronic chest conditions after surgery
- Resolve chronic oedema and hematoma
- Pain relief- muscular pain, neuralgia, tendinopathies, and tendinitis
- Stimulates superficial and deep circulation
- Mobilizes muscle contractures
- General or local relaxation and fatigue relief
CLASSIFICATION OF MASSAGE
- Stroking
It is done with a palmar aspect of the hand alternately. It can be performed in any direction.
The common variations of this technique are superficial and deep, depending on the pressure applied by the therapist, such as Dr. Roshan Jha.
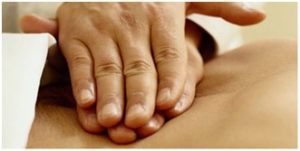
- Effleurage–
This is a slow stroking movement performed with increasing pressure in the direction of flow in the veins and lymphatic channel to drain in lymph nodes.

- Petrissage–
It means “to kneed”. Firm pressure should be applied to the tissue in which the muscle and subcutaneous tissue are alternately compressed and relaxed.
The common variants are kneading, picking up, wringing, and skin rolling.
- Tapotement (Percussion)
“Tapoter” means “to tap”. In this various parts of the hand strikes the tissue at a fairly rapid rate.
The common variants are clapping, hacking, beating, and pounding.

- Vibration & shaking
It a single or double-handed technique in which a fine shaking or tremor is conveyed to the tissue by the hand or fingertips.
The purpose of this Technique is to:
- Loosen the secretions and
- Stimulate the muscle tissues.

- Frictional massage
It should be accurately localized. Deep frictional massage is designed principally to affect the tendons, ligaments, and muscles.
It consists of small, accurately localized deep penetrating movements which are performed in a circular or transverse manner.
‘ At our clinic, frictional massage is an integral part of the treatment program for most tendonitis cases.’
CONTRAINDICATIONS OF MASSAGE
- Large open areas (like burns, wounds)
- Gross oedema
- Marked varicosity
- Areas of hyperesthesia
- Extremely hairy areas
- Chronic swelling in the lower limb associated with congestive cardiac failure or any other cardiac condition.
- Muscular tear, acutely inflamed joints, damaged and diseased blood vessels, skin diseases, skin infections.
For Tapotement techniques –
- Care should be taken for severe rib fracture
- Acute cardiac failure associated with coronary thrombosis
- Severe hypertension
- Hyperesthesia and spasticity/ flaccidity
- Acute pulmonary embolism
- Over newly formed scar tissue
- Acute traumatic oedema
- Cancer/ tuberculosis over the treatment area
For frictional techniques –
- Acute muscle tear
- Acutely inflamed joints
- Skin diseases
- Damaged or diseased blood vessels in the treatment area
- Neoplasm’s/ tuberculosis around the treatment area
- Bacterial infection around the area
We at the Pain Free Physiotherapy Clinic provide Therapeutic massage for different conditions of the back, abdominal, and upper and lower limbs. It is an essential part of our treatment program and in need is given in conjunction with other therapies. Dr. Roshan Jha is highly skilled in different techniques of Massage therapy and patients feel that it’s the best part of our treatment protocol (as per our patient’s feedback).