What is Stress Fracture
It is a common injury in sports as a result of rigorous training. These are tiny cracks in the bone that are not strong enough to undergo the increased intensity of training.
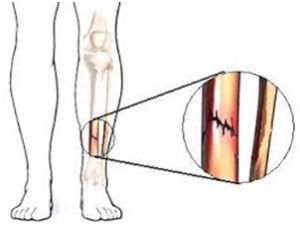
It may affect any bone depending upon the demand for sports. Like that of lumbar vertebrae in gymnasts or Tibial Stress Fracture in runners. It can also arise in normal day-to-day activities in bones weakened because of Osteoporosis.
Stress Fractures occur in 2 scenarios:
- Excessive force through normal bone
- Excessive force through abnormal bone e.g. Osteoporosis
Stress fractures commonly occur in the weight-bearing bones of the lower leg and foot. Track and field athletes are particularly susceptible to stress fractures, but anyone can experience it.
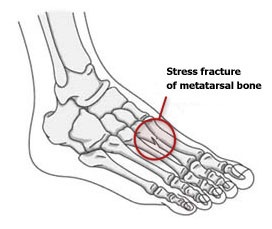
Commonly occurs at the following sites-
- Metatarsal (Foot)
- Navicular (Mid-Foot)
- Tibia (Shin)
- The neck of the Femur (Hip)
- Pars intraarticular (Lower Back – Spondylolysis or Spondylolisthesis)
Causes of Stress Fracture:
The sequences of event that lead to stress fracture are as follows
This is an Overuse injury ⇒ Overtraining/ rapid increase in the intensity of training leads to fatigue⇒ fatigued muscles are unable to absorb excessive load ⇒ the excess load/ stress is transferred to bone ⇒ leads to tiny cracks in the bone called stress fracture.
Women are more susceptible to stress fractures. This can be attributed to a condition called “FEMALE ATHLETE TRIAD”.
- Eating disorders (bulimia or anorexia),
- Amenorrhea (infrequent menstrual cycle), and
- Osteoporosis (reduced bone density).
As a female’s bone mass decreases, her chances of getting a stress fracture increase. The advice of a sports dietitian is highly recommended.
Symptoms:
- Pain with activity is the most common complaint
- The pain subsides with rest.
Diagnosis:
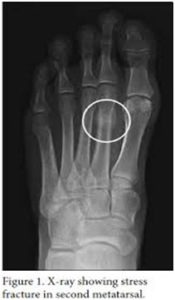
X-rays are commonly used to determine stress fracture. At times x-ray is not helpful as features of a stress fracture on X-ray appear after few weeks. A CT scan or MRI may be needed.
Treatment:
The most important aspect of treatment is rest from the activity that caused the pain. Post-stress fracture engages in Pain-free activities for six to eight weeks. If the provocating activities are not given up it may cause larger and harder to heal stress fracture and in chronic conditions, it may never heal properly.
The Orthopedic doctor will look for bone density, hormonal issues, calcium, Vitamin D, etc, and treat accordingly.
Physiotherapists will analyze the strength, biomechanical faults, training regime and accordingly treat or make necessary changes.
Sports Dietitian will work on the diet of athletes to ensure adequate nutrition.
Prevention:
- Appropriate rest after training
- Gradually increase the intensity of training.
- Cross-training – alternating activities that fulfill the same fitness goals.
- Apart from maximizing the mainstream training like endurance in marathon runners, athletes should also be trained to achieve optimal levels of strength and power.
- Maintaining a healthy diet.
- Use appropriate footwear.
- If pain or swelling occurs, immediately stop the activity and consult a physiotherapist or orthopedic doctor.