Mobilization
Mobilization may be applied as an oscillatory movement or a sustained stretch intended to decrease pain or increase mobility.
It can be broadly classified into two types-
- Physiological and
- Accessory movement
Physiological movements are visible movements by different parts of the body and can be done voluntarily by an individual e.g. Flexion-Extension.
Accessory movements are intra-articular movements. It can be further divided into 2 types,
- Component motion and
- Joint play
Component motion: These are movements within the joint and surrounding tissues that are necessary for normal range of motion but cannot be actively performed by the patients i.e. not under the voluntary control of an individual.
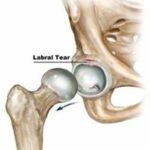
Joint play: Motion that occurs between the joint surfaces as well as distensibility in the joint capsule which allows the bones to move e.g. distraction, sliding, compression, rolling, and spinning of joint surfaces.
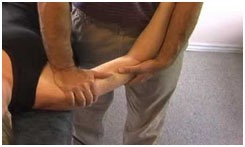
What are the indications of joint mobilization?
1) Pain, muscle guarding, and spasm
- Neuro-physiological effect–
Small amplitude oscillatory and distraction movements are used to stimulate the mechanoreceptors that may inhibit transmission of nociceptive stimuli at the spinal cord and brain stem level. - Mechanical effect–
Small amplitude distraction or gliding movement of a joint is used to cause synovial fluid motion, which in turn brings nutrition to avascular portion.
- Neuro-physiological effect–
2) Reversible joint hypo-mobility
It can be treated with progressive vigorous joint play technique to elongate hypomobile ligaments and capsular connective tissue.
3) Progressive limitation (chronic stage of hypomobility)
This can again be treated with joint play technique at a higher grade of mobilization and integration of other special and advanced techniques.
4) Functional immobility
This can be treated with non-stretch gliding or distraction techniques.
5) Positional faults
CONTRA-INDICATIONS OF MOBILIZATION
- Hyper-mobility
- Fractures (acute)
- Joint effusion
- Inflammation of joint
Precautions of joint mobilization:
Under the following, conditions mobilization should be either not done too vigorously or not done at all to nearby joints.
- Malignancy
- Bone disease
- Unhealed fractures
- Excessive pain
- Total joint replacement
- Newly formed or weakened connective tissue such as the following surgery, injuries.
- Disuse injury or when a patient is on corticosteroid.
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Elderly individuals with weakened bone.
Manipulation
These are skilled, gentle precise passive movements of a joint either within or beyond its active range of motion (or physiological limits). This is often accompanied by an audible ‘crack’.

This can be categorized into-
- Thrust manipulation (HVT- High-velocity thrust) – performed at high velocity, the small amplitude at end range.
- Manipulation under anesthesia – performed under anesthesia by an orthopedic surgeon to increase the range.
We at the pain-free physiotherapy clinic are specialized in treating hypomobile joints post-fracture or post immobilization. Any flexible positional faults or movement restriction of the spine or other joints can be effectively treated post careful evaluation. Contact us to get free from movement restriction.
Various manual joint mobilization techniques used are mentioned and discussed briefly under Manual Therapy.