Acute Low Back Pain
Back pain is one of the most common medical problems, affecting 9 out of 10 people at some point during their lives. It can range from a dull, constant ache to sudden, sharp pain. This pain or discomfort can happen anywhere in the back, the most common area affected is the lower back. This is because the low back supports most of the body’s weight. Acute back pain comes on suddenly and usually lasts from a few days to a few weeks. Back pain is called chronic if it lasts for more than three months.
Acute Low Back Pain is most often caused by a sudden injury to the muscles and ligaments supporting the back. The pain may be caused by muscle spasms or a strain or tear in the muscles and ligament
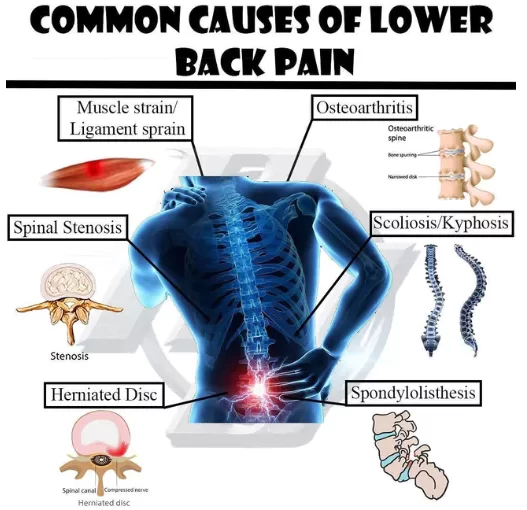
What are the Causes of Sudden Low Back Pain?
- Compression fractures to the spine from osteoporosis
- Cancer involving the spine
- Fracture of the spinal cord
- Muscle spasm (very tense muscles)
- A ruptured or herniated disk
- Sciatica (numbness/ tingling running down the leg)
- Spinal stenosis (narrowing of the spinal canal)
- Spine curvatures (like scoliosis or kyphosis), which may be inherited and seen in children
- Strain or tears to the muscles or ligaments supporting the back
Chronic Low Backache
It may result from arthritic (wear and tear that occurs over the year) changes, which may be due to –
- Heavy use from work or sports
- Past injuries and fractures
- Surgical intervention of the spine in the past
- Discal changes over the years resulting from herniation of the disc which once upon a time was an acute problem
Other causes can be
- Long-standing cases of scoliosis and kyphosis
- Medical problems, such as fibromyalgia, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis
- Spondylosis and Spondylolisthesis.
Common Symptoms of Low Back Pain:
Low back pain can vary widely. The pain may be mild, or it can be so severe that one is unable to move. A variety of symptoms depending upon the cause can appear in the back, buttock region, and thigh and at times till toes. The patient may have a tingling or burning sensation, a dull achy feeling, or sharp pain, weakness in legs or feet.
People at greater risk for low back pain are:
- above 30 years of age
- Overweight
- Pregnancy
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Stressed or depressed
- have to do a lot of heavy lifting, bending, and twisting, or that involves whole-body vibration (such as truck driving)
- Smoking
How to take Care of your Back at Home?
A common myth about back pain is that the patient needs to rest and avoid activity for a long time. In fact, complete bed rest is not recommended, rather an active rest is needed. If there are no signs of a serious cause for back pain (such as loss of bowel or bladder control, weakness, weight loss, or fever), stay as active as possible.
Here are some Tips for how to handle Back Pain and activity:
- Stop normal physical activity for only the first few days. This helps calm the symptoms and reduce swelling (inflammation) in the area of the pain.
- Apply heat or ice to the painful area. Use ice for the first 48 to 72 hours, and then depending on the pain level hot or cold therapy can be decided.
- You may also use Turmeric for Back Pain.
- NSAIDs can be taken during the initial inflammatory phase by the recommendation of a physician
- One can sleep in a curled-up, fetal position with a pillow between the legs. While sleeping on the back pillow can be placed underneath the knees.
- Activities involving heavy lifting or twisting of the back for the first 6 weeks after the pain should be avoided.
- Exercise during painful days should be avoided. After 2 to 3 weeks, as pain goes, exercises can be resumed again.
Physiotherapists at PAIN-FREE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC can teach you which exercises are right for you. Contact us to know your back problem better and the best possible treatment for your pain.
A complete exercise program should include aerobic activity (such as walking, swimming, or riding a stationary bicycle), as well as stretching and strength training. Follow the instructions of the physiotherapist.
Begin with light cardiovascular training. Walking, riding a stationary bicycle, and swimming are great examples. These types of aerobic activities can help improve blood flow to the back and promote healing. They also strengthen the muscles of the stomach and back.
Stretching and strengthening exercises are important in the long run. Keep in mind that starting these exercises too soon after an injury can make the pain worse. Strengthening the abdominal muscles can ease the stress on the back.
Physiotherapists at our clinic can help you determine when to begin stretching and strengthening exercises and how to do them.
Avoid the exercises mentioned below during recovery, unless the physiotherapist gives a go-ahead sign.
- Jogging
- Contact sports
- Racquet sports
- Golf
- Dancing
- Weight lifting
- Leg lifts when lying on the bed
- Sit-ups
Measures to Prevent Future Low Backache
To prevent Lower back pain, proper lifting, and bending techniques should be learned. Follow these tips:
- If an object is too heavy or awkward, get help.
- Spread the feet apart to have a wide base of support.
- Stand as close as possible to the object to be lifted.
- Bend at the knees, not at the waist.
- Tighten the stomach muscles while lifting or lowering the object.
- Hold the object as close as possible to the body
- Lift using the leg muscles.
- While standing up with the object in hand, do not bend forward.
- Do not twist while in a bending position to reach for the object, lifting it up, or carrying it.
Other measures include:
- Do not wear high heels. Wear shoes that have cushioned soles when walking.
- While sitting, especially if using a computer, make sure that the chair has a straight back with an adjustable seat and back and armrests.
- Use a stool under the feet while sitting so that the knees are leveled to the hip.
- Use a small pillow or roll behind the lower back while sitting or driving for long periods.
- While driving long distances, stop every hour and walk around for a few minutes. Do not lift heavy objects just after a long ride.
- Quit smoking.
- Lose weight.
- Do exercises to strengthen the abdominal muscles. This will strengthen the core to decrease the risk of further injuries.
- Learn to relax. Try methods such as yoga, tai chi, or massage.
Back pain can be sub-categorized according to the structures involved-
1- Muscle-related pain
- Back Cramps
- Core Stability Deficiency
- DOMS – Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness
- Fibromyalgia
- Side Strain
2- Back Bone-related pain
- Stress Fracture
- Osteoporosis
- Scheuermann’s Disease
- Scoliosis
- Spinal Stenosis
- Spondylosis
- Spondylolysis
- Spondylolisthesis
3- Disc-related pain
- Slipped Disc – Herniated Disc (PIVD)
- Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD)
4- Facet Joint arthropathy
5- Nerve-related pain
- Nerve entrapments
- Sciatica
6- Pelvis-related pain
- Sacroiliac Joint Pain
- Piriformis Syndrome
7- Systemic Diseases
- Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
Suffering From Low Back Pain or have questions regarding the problem? Do not hesitate, Call us now.